Using a noise bridge to measure coaxial-cable impedance
In Transmission Line Transformers,(1) Jerry Sevick, W2FMI, describes a simple method of measuring the characteristic impedance of a transmission line. This method makes use of the fact that when a cable is terminated in a resistance equal to the cable's characteristic impedance, the cable looks like a pure resistance. But when the cable is terminated in a resistance of a different value, the cable appears reactive. The null of a resistance bridge is very sensitive to the reactive component. When looking at a pure resistance, the bridge gives a deep null; if reactance is present, the null is shallow. This method of measurement is accurate and is invaluable when making parallel or twisted-wire lines for balun transformers.
Sevick uses a simple resistance bridge with a signal source and detector. It's also possible to make the same measurements using a noise bridge and a receiver. I tried this and was impressed with the accuracy I obtained.
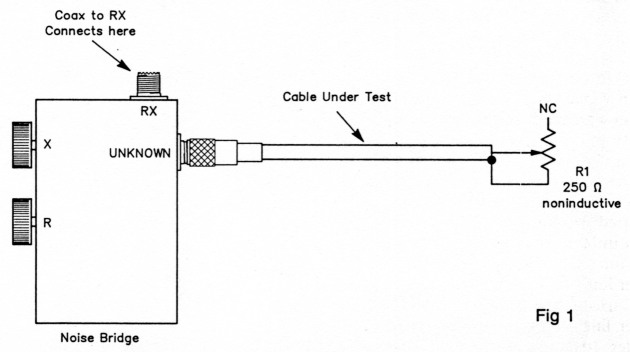
Fig 1 shows the test setup. Here's the procedure:
- Tune the receiver to the measurement frequency. (Sevick suggests working at frequencies between 10 and 20 MHz.)
- Connect a 50-0 load to the UNKNOWN terminal of the noise bridge. Carefully adjust the X (or reactance) knob setting for a deep null in the noise. Hereafter, don't change the X knob setting.
- Remove the resistor from the UNKNOWN terminal and connect the cable under test (CUT) to that terminal. (You can measure a whole roll of cable, or a sample piece just a foot or two long.)
- Set the noise bridge R (resistance) knob at the resistance corresponding to the characteristic impedance you expect to find.
- Adjust R1 for a null.
- Change the setting of the R knob.
- Repeat steps 5 and 6 until you find the deepest null. As you approach the cable impedance, the null gets deeper. If you go beyond it, the null again becomes shallow.
- After finding the deepest null, read the noise bridge R dial, or measure the resistance of R1. The result obtained is the cable's impedance.
K6NY, Jack Althouse.